And how just a few letters in the code fitting a generalized linear model mean the difference between extracting one or the other There are plenty of other explanOdds Ratio (OR) The difference between odds and probability is important because Relative Risk is calculated with probability and Odds Ratio is calculated with odds Relative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of oddsRisk = odds/ (1odds) "Most published research providing an odds ratio as a measure of effect size should also provide sufficient information for the baseline risk, and hence the relative risk, to be calculated If numbers in each group are given, the crude relative risk can be calculated directly" – BMJ 14;348f7450 doi /bmj

Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice
Relative risk vs odds ratio
Relative risk vs odds ratio-RR=OR/ ( (1−Pref) (Pref∗OR)) RR = risk ratio;The person would have about a 1% chance of a heart attack if they didn't improve their health In both cases the relative risk was 5, but with entirely different levels of impact Please note this example is not meant to be interpreted that taking care of your health is not important!!!




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk
Figure 1 Relationship between Odds Ratio and Relative Risk for various incidence rates 38 8 166 Int J Public Health 53 (08) 165–167 When to use the odds ratio or the relative risk?Risk vs odds The terms 'risk' and 'odds' are often used interchangeably but they actually have quite different implications and are calculated in different ways Odds is a concept that is very familiar to gamblers It is a ratio of probability that a particular event will occur and can be any number between zero and infinityAnother measure we can find is odds
Risk is often a more intuitive concept than odds, and thus understanding relative risks is often preferred to understanding relative odds However, OR does not suffer from the same causal assumption limitations as RR, making it more widely applicableOR = odds ratio;RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO Risk and Odds just seemed the same to me for a long time Since then, I have come to understand to important difference Lets start with Relative Risk Relative Risk can be addressed by asking the following question How many times more likely is an exposed group to develop a
Odds ratio or relative risk While there is a conceptual relationship between these measures, they are still different enough that you should probably report separate pooled estimates for the studies using a hazard ratio and the studies using odds ratios/relative risks Steve Simon, Standard DisclaimerThe difference between odds ratio and risk ratio • ericminikel The other day I was emailing with a statistical genetics colleague about a rare SNP associated with a phenotype I stated that the minor allele frequency (MAF) was 07% in cases and 01% in controls, for a risk ratio of 7 After clicking send, I felt a twinge of regretThe odds ratio and the relative risk will not always disagree by this much Large effects on groups with high initial risk seem to cause the most problems See Davies et al (1998) for some useful guidelines for when the odds ratio and relative risk are likely to differ When they do differ, the relative risk represents the typical interpretation



Pdf The Relative Merits Of Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Semantic Scholar




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
1 The odds of having the disease in the exposed group arePortantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998) And it is this fact that enables us, most of the time, to approximate the relative risk with the odds ratio Table 5 below illustrates the relationship between RR and OR for some probabilities of the outcomeSee all my videos at https//wwwzstatisticscom/videos/Health Stats IQ playlisthttps//youtubecom/playlist?list=PLTNMv857s9WUI5YsQMW14trmbopjZMWPa000 Int




Wasp Write A Scientific Paper Using Excel 12 Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Sciencedirect




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id
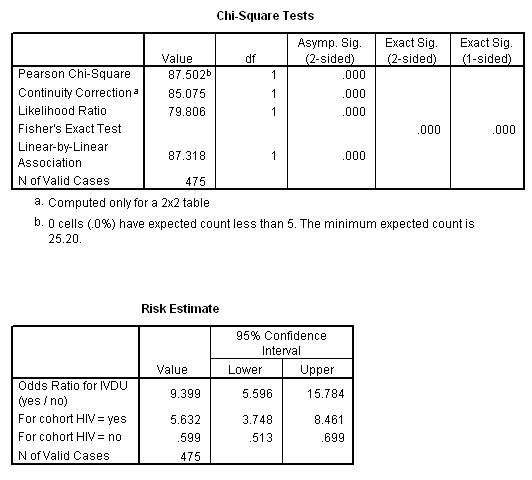
Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratioRelative Risk (RR) &It is assumed that, if the prevalence of the disease is low, then the odds ratio approaches the relative risk Case control studies are relatively inexpensive and less timeconsuming than cohort studies In this case the odds ratio (OR) is equal to 16 and the relative risk (RR) is equal to 865




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



Marg Innovera
Why are the relative risk and odds ratio approximately equal?Relative Risk and Odds Ratios In the population under investigation, relative risk refers to a ratio between members of the population expressing the trait of interest (eg cancer), with distinction made between whether or not those members had previously been exposed to a related riskRE st odds ratio vs RRR in multinomial logistic regression Thanks this is very helpful One more question With odds ratios in binary logistic regression, you can easily interpret the exponentiated coefficient by stating that the odds of outcome 1 are 24 times greater than the odds of outcome 2 When I expoentiate the coefficient in




Beabletocalculate Direct Age Adjustment Chegg Com




Relative Risk Analysis And Odds Ratio Analysis
The odds ratio is extremely important, however, as it is the only measure of effect that can be computed in a casecontrol study design When the outcome of interest is relatively rare (<10%), then the odds ratio and relative risk will be very close in magnitudeThe basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk isRelative risk, odds ratio, risk ratio, risk difference these are all measures of the direction and the strength of the association between two categorical variables Can I




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像
Relative Risk vs Odds ratioOdds ratio vs Relative Risk/Hazard Ratio I have a background in physics with a few courses in statistics, but I still have a hard time intuitively understanding OR I get RR as it just is a ratio of probabilities, and I look at HR as RR with a time componentThis post tries to explain the difference between odds ratios and relative risk ratios;



Statistics Basics Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Calculation In Excel Bi Practice




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 1 by the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 2The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed groupSince relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effectiveness, the distinction is important especially in cases of medium to high probabilities If action A carries a risk of 999% and action B a risk of 990% then the relative risk is just over 1, while the odds associated with action A are more than 10 times higher than the odds with B




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice
Relative survival and causespeci c survival attempt to estimate Hazard Ratio Age group Causespeci c HR Pvalue 95% CI 1859 100 hazards is the risk setFor the causespeci c hazard the risk set decreases each time there is a death from another cause censoring Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literatureUnderstanding Relative Risk, Odds Ratio, and Related Terms As Simple as It Can Get Chittaranjan Andrade, MD ABSTRACT Risk, and related measures of effect size (for categorical outcomes) such as relative risks and odds ratios, are frequently presented in research articles Not all readers know how these statisticsYou may have noticed that the odds ratio and relative risk are very similar in this case This happens when the proportions being compared are both close to 0 Which one you decide to use is a matter of personal preference and perhaps your audience




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction becomes important in cases ofThe odds ratio (OR) is a ratio of 2 numbers, like the relative risk we have 3 options OR = 1 The odds in the first group are the same as those in the second So no evidence that drinking wine can either OR >ELI5 odds ratio vs relative risk Google search has plenty, but none are ELI5 I'm reading a medical journal which says if a baby poops in the amniotic sac (meconium), the odds ratio for it having problems after birth (respiratory, heart, etc) is 364




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology
The risk of failure with SF was 96/351 (27%) vs 32/350 (9%) with HP The RR was 3 This has a very intuitive meaning risk of failure with SF was three times more likely than HP Odds Ratio The OR is a way to present the strength of association between riskOdds Ratio vs Relative Risk What's the Difference?Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a r



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Solved Youll Need To Know Prevalence Rate Odds Ratio Chegg Com
Relative risk is actually the ratio between incidence of outcome/disease among exposed people and that among unexposed people It is usually used in a cohort study where there is a definite population under study and we can calculate incidence rates Hence it is a direct and accurate value compared to odds ratioThe literature dealing with the relation between relative risk and odds ratio is quite exten sive (some examples are (Da vies et al, 1998;Risk is often a more intuitive concept than odds, and thus understanding relative risks is often preferred to understanding relative odds However, OR does not suffer from the same causal assumption limitations as RR, making it more widely applicable




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
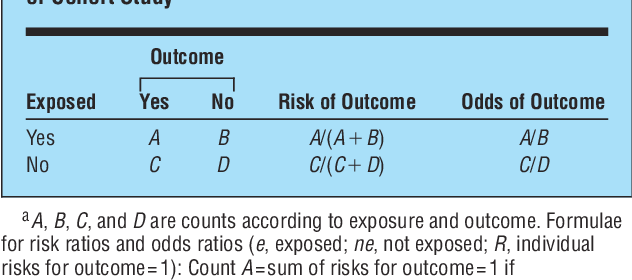
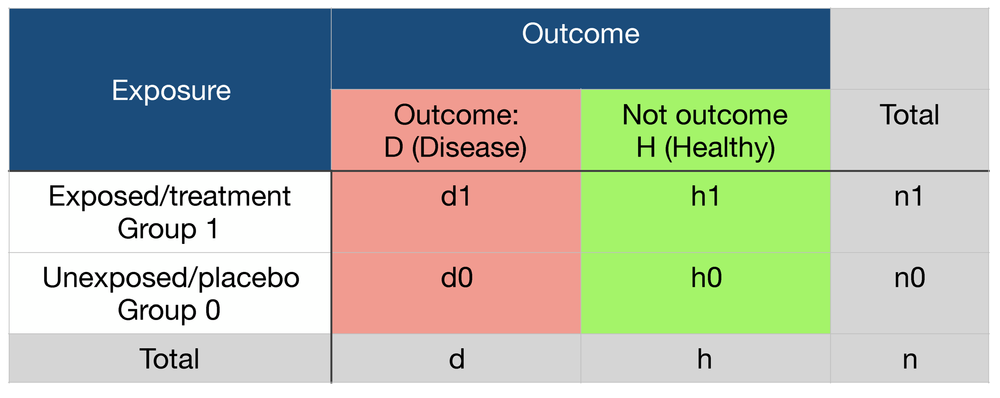
RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO The relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other groupPref = Prevalence of the outcome in the reference group oddsratio relativerisk Share Improve this question edited May 24 at 1733 kjetil b halvorsen ♦ 59k 23 23 gold badges9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects




Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to the treatment Odds is the number having the outcome divided by the number not having the outcome The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control groupClick on the article title to read more1 Answer1 Odds ratio and relative risk are two measures used to describe the likelihood of an event happening The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of an event or disease occurring in one group to the odds occurring in another group The standard formula is X / ( 1 − X) / Y / ( 1 − Y), where X and Y are the probability




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



1
Odds ratio relative risk Relative risk An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds Relative risk isRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy
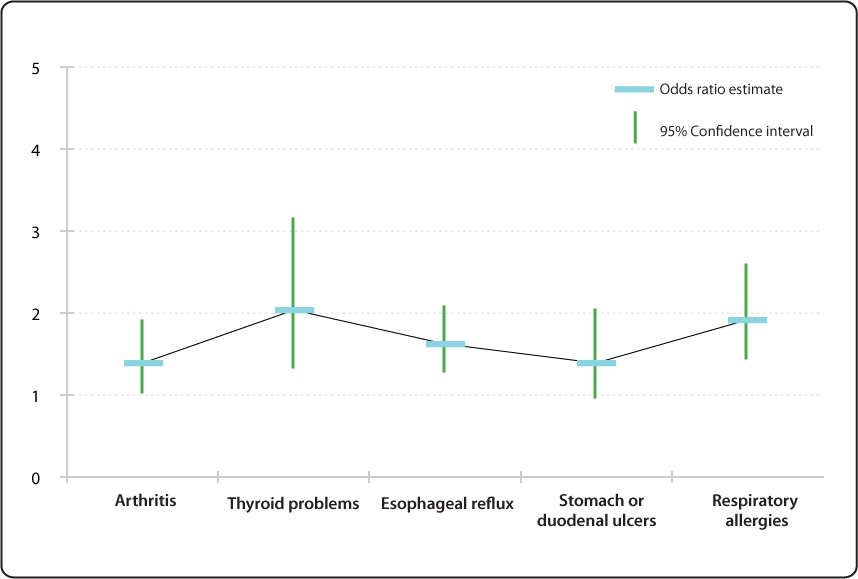



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals For People To 66 Years Of Age And With Selected Conditions Ever Having Voice Problems Or Disorders Nidcd




Measuring Of Risk




Solved Present Example Of An Dolds Ratio Compared To A Chegg Com




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj




Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Incidence Download Scientific Diagram




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table




Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



Relative Risk Odds Ratio



1




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




What Are Cross Tables Odds Ratio And The Relative Risk Gcp Service




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Solved Select All Of The True Statements Regarding The Odds Chegg Com




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International
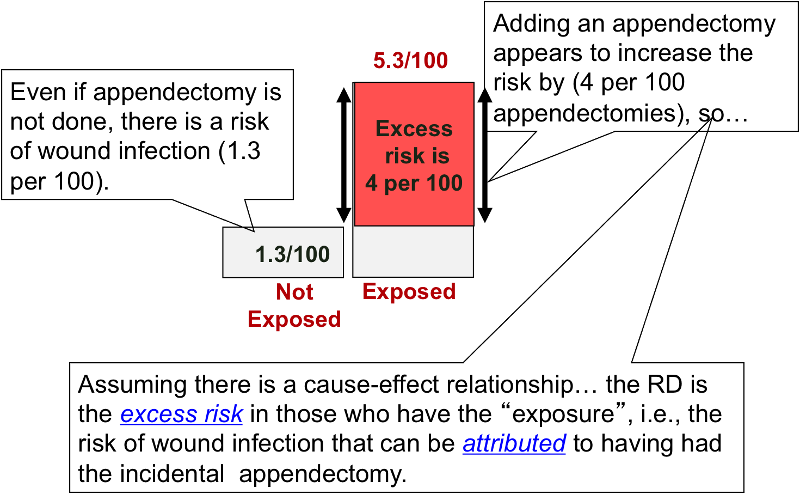



Risk Differences And Rate Differences




First Aid Epidemiology Biostatistics Flashcards Quizlet



Epidemiology Stepwards



6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream
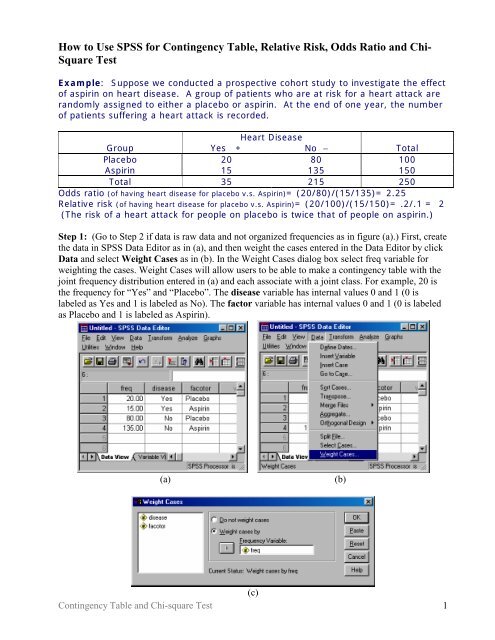



How To Use Spss For Contingency Table Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Solved Activity 4 Identification Of Risk Relative Risk Chegg Com




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Odds Vs Risk Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology




Literature Search




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey



1



Odds




Reporting The Results Sage Research Methods



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream
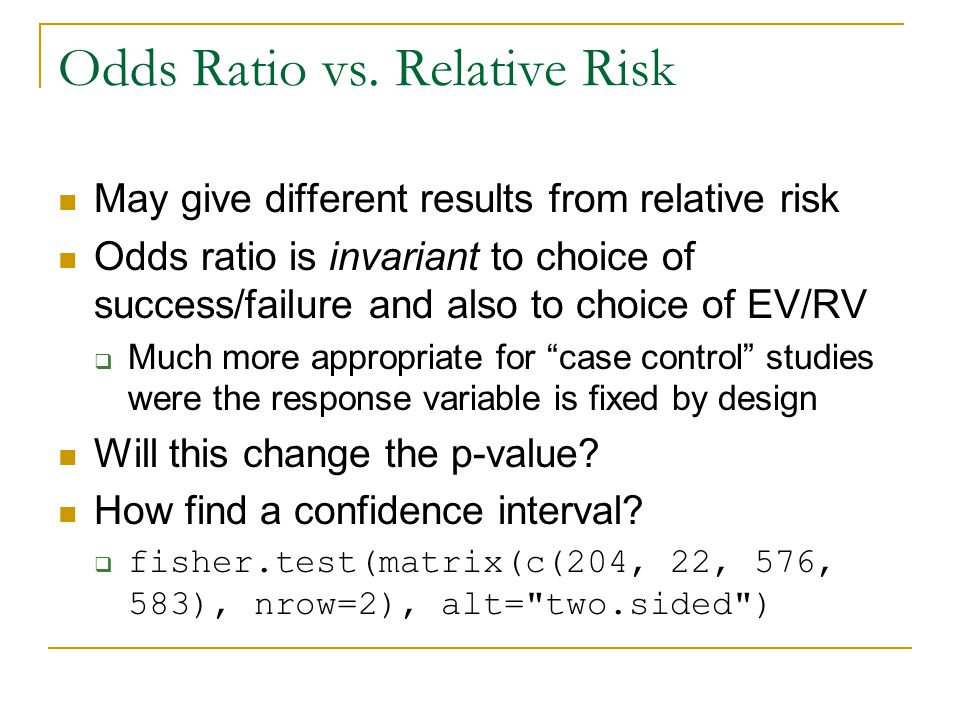



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Ratio And Why It Matters Youtube




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube



Github Flor3652 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Shiny App




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram




Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Extensive Video Youtube




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Forest Plots Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Detecting Fecal Download Scientific Diagram
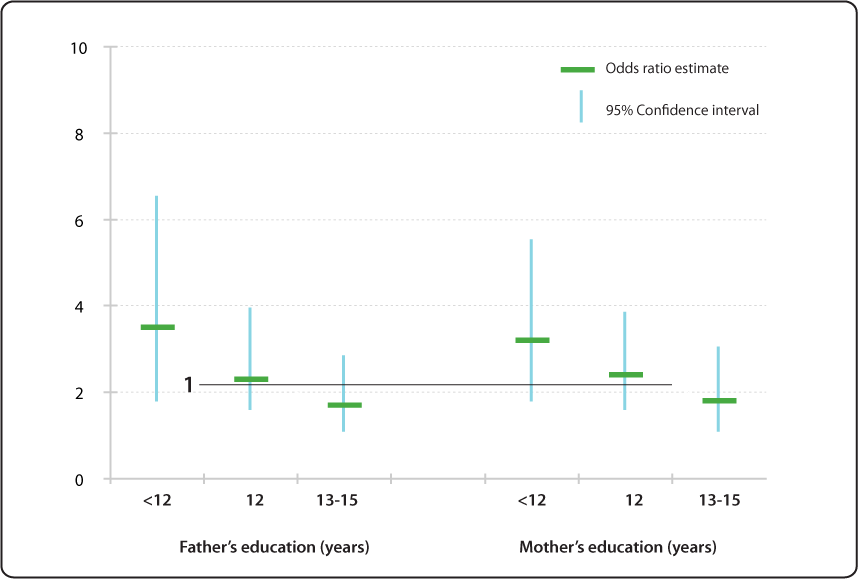



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals Of Children Having Specific Language Impairment Sli By Parent S Level Of Education Reference College Graduate Or More Education 16 Years Nidcd




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1 How To Memorize Things Math Notes Public Health Jobs




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table



9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Odds Ratios Are Calculated From Case Control Studies Which Are Described On Slide 14 Odds Ratios Are Only Estimates Of Relative Risks Since True Incidence Rates Cannot Be




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿